After onset, psoriasis in most patients does not go away on its own, but only progresses and becomes wider, spreading over the skin.
However, with timely diagnosis, it becomes easier to treat and recovery comes much faster.
The main thing here is to pay attention to the first signs of psoriasis in time and immediately make an appointment with a dermatologist.
Characteristic signs of psoriasis
Early psoriasis may present as small, reddish, scaly patches.
The site of occurrence of such rashes depends directly on the form in which the disease persists.
In most cases they can be seen:
- on elbows and knees;
- on the head (in the hairy area);
- on the palms and soles;
- in the fold area (buttocks, armpits, under breast area in women).
Primary eruptions (papules) are very small in size: their diameter does not exceed 4 millimeters.
However, as the disease progresses, they enlarge and coalesce with each other, forming plaques that do not have a clear shape.
Most often, the appearance of papules is not accompanied by pain or itching. The feeling of discomfort increases with the development of psoriasis and an increase in the size of the affected areas of the skin.
The affected area begins to ache and itch, and there is a strong burning sensation.
These signs of psoriasis are complemented by emotional disturbances that can significantly increase the rate at which the disease spreads.
It is inappropriate to start self-treatment when such rashes are found, as psoriasis in the early stages of development is similar to other skin diseases.Therefore, the wrong choice of medication will not lead to positive results, but will only worsen the situation.
Cumulative Symptoms
Scaly lichen belongs to the category of systemic pathologies.
This means that it manifests not only on the skin and nails, but can also affect the spine, joints and tendons, certain body systems (for example, endocrine, immune and nervous).
There have been cases when the disease affects the digestive (liver) and urinary (kidney) systems.
The first symptoms of psoriasis
- constant feeling of tiredness;
- weakness;
- a state of depression (up to depression).
Due to the complex effect of the disease on the body, experts consider it appropriate to call it psoriatic disease.
But despite this, the main aspects of the disease are based on skin damage.
As mentioned above, the first call for the onset of pathology development are small papules in the color range between pale pink and red.
They differ in a symmetrical position on the surface of the skin (folds, lower back, hair-covered area of the head), sometimes - in the mucosa of the external genitalia.
The size of the papules in the further course of the disease can exceed 10 centimeters.
Psoriatic outbreaks, depending on their characteristics, are divided into:
- with dots (their size is not larger than the head of a peg);
- teardrop-shaped (teardrop-shaped, equivalent in size to a lentil grain);
- in the form of coins (plates with a diameter of 5 mm, have rounded edges);
- Rarely arched, annular or map-like.
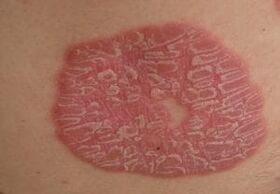
Above the papules are covered with scaly plaques, which are formed by keratinized cells of the epidermis and removed without much effort. Initially, they appear in the center of the plate and gradually spread further and further.
Keratin cells have air gaps, which results in visual sensitivity and light shading.
Sometimes the elements are surrounded by a pink ring that acts as an area of plaque growth and inflammation. In this case, the condition of the surrounding skin does not change.
Tile removal reveals a glossy, deep red surface based on capillaries, which in turn have very thin walls.
The presence of such small vessels in diameter is due to damage to the structure of the upper layers of the skin, the structure of which is broken due to the incomplete maturation process of epidermal cells (keratinocytes), whichwhich makes it impossible to differentiate them accurately.
Symptoms of various forms of psoriasis
Common psoriasis has fairly specific symptoms, so it will not be difficult to diagnose.
Looks like scaly, rounded areas that protrude above normal skin and are pink or red.
Sometimes, in the early stages of the disease, there are no typical plaques: small papules can be seen before they appear on the scalp and in the joint area (ankle, elbows and knees).
They are able to persist for quite a long period of time and not cause any discomfort to the patient: nothing is itching and there is no pain or no pain at all, or practically not felt, the papules themselves are almost impossible toobserved.
They do not peel, but when lightly scratched, the scales appear immediately. Such pink seals may disappear or decrease significantly in size during the summer, as sunlight affects the skin.
The acute form of common psoriasis manifests itself in the form of numerous constantly itchy rashes of brightly colored papules and is the result of the influence of factors that activate the disease.
To avoid his mistake for an allergic reaction, you should scratch the surface of the tile just before the characteristic phenomena appear.
Seborrheic psoriasis starts on the scalp (in the area covered with hair) and then spreads to the face and shoulders.
Characterized by the heavy skin of the relevant area, which is most often assessed by patients as dandruff, so they do not rush to the dermatologist.
This fact allows the disease to quietly reach the developmental stage when the forehead and areas behind the ears are peeled off. And only after the tiles are created.
Lesion of the skin folds with psoriatic disease (armpits, genital area and groin, under the breast in women) is often confused with the usual irritation caused by rubbing or sweating.
This type of disease is characterized by smooth plaques that look like spots. Peeling is not noticeable, but they often get wet. The blushes themselves are bright red, they are even and shiny.
In case of damage to the genitals, the characteristic signs of psoriasis can be misinterpreted as balanoposthitis (lesions of the head of the penis, as well as the foreskin on the inside of it) in men and vulvitis (redness localized in the labia minora)in women.
The palmar-plantar form of the disease appears in the form of compacted areas, similar to calluses, the surface of which is covered with yellow scales that are difficult to remove.
Affected areas are cracked and injured. With this form of the disease, it is difficult to induce the appearance of a terminal film and bloody dew by clearing.
Nail psoriasis begins with psoriatic onychodystrophy, which is one of the main symptoms of this form of the disease and appears much earlier than rashes.In the early stages, the edge of the nail is covered with grooves and small depressions.
As the disease progresses, they spread, reaching the root, after which there are changes in its color. The nail dulls and thickens. Due to failures in blood circulation, the manifestation of the disease increases.
Epidermal cells accumulate under the nail plate and are bordered by fried tissue on all sides, after which it can be peeled off after a while.
This type of psoriasis is dangerous because it increases tissue sensitivity, which, in turn, increases the likelihood of infection. Too often, this disease is mistaken for a fungus.
The moving joints of the bones (joints) are often affected. They are deformed, the joint capsule undergoes dystrophic type modifications.
Psoriatic arthritis begins with an increase in joint volume, which is accompanied by pain.
The fingers of both hands and feet are more susceptible to this type of psoriasis.
In severe forms, the shoulder and elbow joints, hip and knee, as well as some parts of the back, are exposed to the disease.
Effect on the onset of symptoms of psoriasis stages
The symptoms of psoriasis are in direct proportion to the season of the year and the stage at which the disease is.
Most often in the spring-summer period there is a noticeable decrease in disease activity, which is facilitated by ultraviolet rays.
Therefore, in the autumn-winter period due to lack of sun, the disease is rapidly gaining momentum. There are virtually no patients with summer exacerbations.
There are three stages of psoriasis:
- progressive- characterized by the constant appearance of new rashes, an increase in the size of previously appearing plaques and their pink border surroundings, the affected area is very itchy andshaky;
- immobile- new rashes no longer appear and old ones do not grow; the upper layer of skin in the area of the plates becomes wrinkled;
- regressive- the skin does not peel, the plaques disappear, leaving behind highly pigmented areas.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
Diagnosis of psoriasis is made on the basis of information obtained from a medical examination interviewing a patient, as well as symptoms inherent in one form or another of the disease.
The sooner a disease is detected, the sooner the treatment process begins. Therefore, more tangible results will be obtained.
Due to the fact that the picture of the disease is extremely specific, the diagnosis of psoriasis can be limited to a simple examination by a dermatologist.
But in some cases, difficulties may arise due to implication or lack of symptoms, which occurs if the disease does not appear in any way or seems uncharacteristic. This situation requires further research procedures.
A specific method is used to make the diagnosis, which consists of the gradual scraping of the papule along the layer.
As a result of such manipulation, it is possible to identify the characteristic signs (psoriatic triad) for differentiating psoriasis from other diseases and establishing a definitive diagnosis:
- stearine stain;
- terminal film (pink epidermal cells);
- blood dew (drops of blood appear on the surface of the plaque due to rupture of capillaries).
If necessary, the patient is tested in the form of affected tissue samples.
X-rays are taken if psoriasis-related arthritis is suspected.
If psoriasis is at an early stage, its diagnosis is not difficult: the appearance of osteoporosis is clearly visible.
In later periods, there is a narrowing of the joint space, erosion of bone-forming tissues, osteosclerosis and periostitis.
If the disease is severe, the ankle joints and metatarsal joints are destroyed, as a result, the joint completely loses its mobility.
It should be noted that all tests performed are necessary not only for the final diagnosis, but also for differentiation with other diseases, which, at first glance, are identical.
These diseases include: parapsoria, seborrheic eczema, lichen rosacea, atopic dermatitis, lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and others.























